1. E-business Applications Infrastructure
Applications that provide access to services and information inside beyond an organization. That is the architecture of hardware, software, databases, and content used to deliver e-business services to employees, customers, and partners.
Examples : CRM, Supply Chain Management, Data Mining, Content Management Systems.
2. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Applications
Software providing integrated functions for major business functions such as production, distribution, sales, finance, and human resources management. For example, vendors such as SAP & Oracle provides ERP Applications.
3. Service Oriented Architecture (SOA)
A service-oriented architecture is a collection of services that communicates with each other as part of a distributed systems architecture comprising different services. This is an arrangement of software processes or agents that communicate with each other to deliver the business requirements. The main purpose of SOA is to provide functionality.
4. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
The exchange, using digital media, of structured business information, particularly for sales transactions such as purchase orders and invoices between buyers and sellers. The types of documents exchanged by EDI include business transactions such as orders, invoices, delivery advice, and payment instructions.
Clarke (1998) defines EDI as :
the exchange of documents in standardised electronic form,between organisations,in an automated manner,directly from a computer application in one organisation to an application in another.
clarke,1998.
5. Electronic Procurement System (EPS)
An electronic system used to automate all or part of the procurement function by enabling the scanning,storage and retrieval of invoices and other documents; management of approvals; routeing of authorization requests; interfaces to other finance systems; and matching of documents to validate transactions.
For example, online entry, authorization and placing of orders using a combination of data entry forms, scanned documents and email based workflow.
6. Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
Marketing with the help of Search Engines. Search Engines provide an index of content on registered sites that can be searched by keyword. They are the primary of finding information about a company and it’s products. It follows that if an organization is not prominent in the search engines, then many potential sales could be lost. Since a company is dependent on the strength of its brand and offline communications to drive visitors to the website.
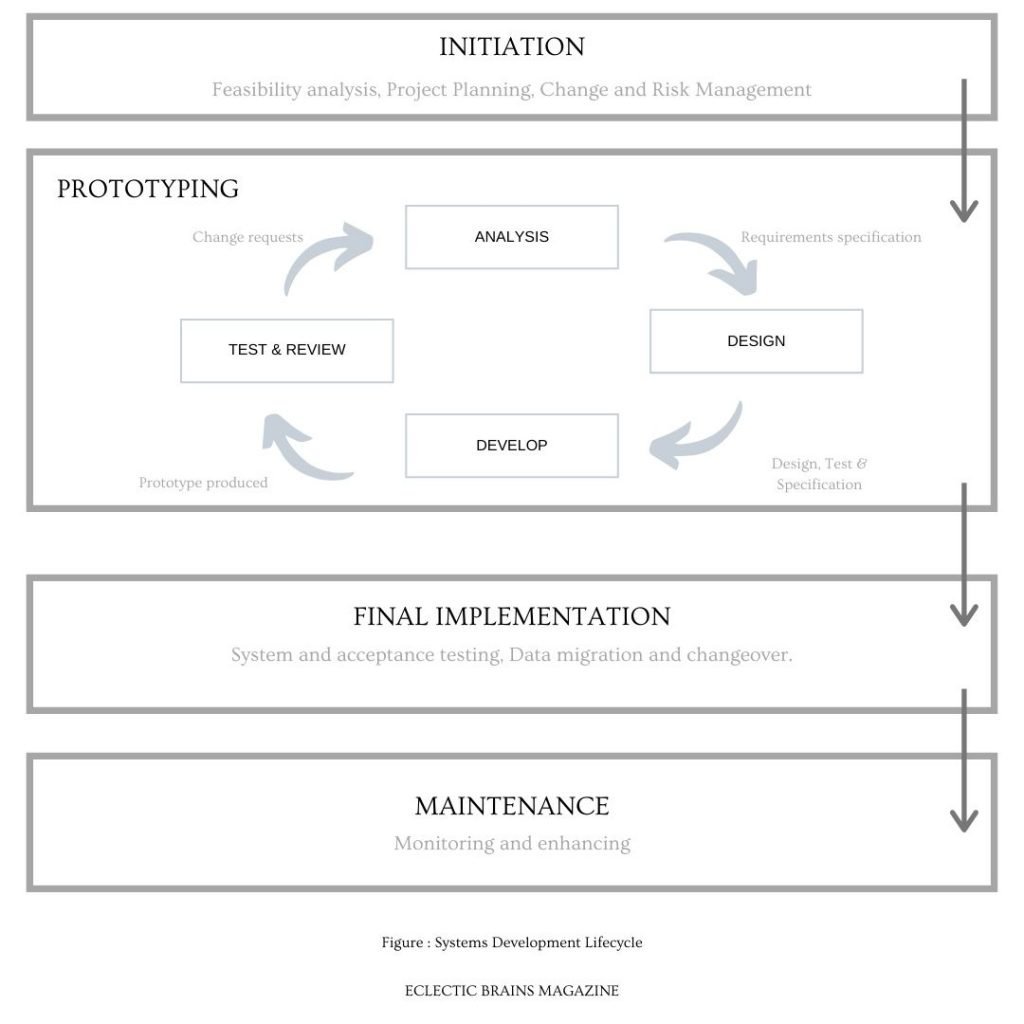
7. Systems Development Life cycle
The sequence in which a system is created from initiation, analysis, design, implementation, build, and maintenance.
8. Electronic Customer Relationship Management (eCRM)
Electronic Customer Relationship Management is using digital communications technologies to maximize sales to existing customers and encourage continued usage of online services. For example, eCRM includes activities as :
- Using the website for customer development from generating leads.
- Managing email list quality.
- Applying e-mail marketing to support upsell and cross-sell.
- Data Mining to improve targeting
- Personalization for products.
- Providing online customer service facilities.
- Managing the multi-channel customer experience as customers use different media as part of the buying process.
9. Customer Acquisition Management
Techniques used to gain new prospects and customers. For example, use of the website to acquire new customers for a company as qualified leads that can be hopefully converted into sales. It also means to encourage existing customers to migrate to using online for a purchase or service.
10. Cross-Media Optimization Studies (XMOS)
Cross-Media Optimization Studies to determine the optimum spend across different media to produce the best results. XMOS research is designed to help marketers and their agencies answer the question “What is the optimal mix of advertising vehicles across different media in terms of frequency,reach and budget allocation, for a given campaign to achieve its marketing goals?” The mix between online and offline spend is varied to maximize campaign metrics such as reach, brand awareness and purchase intent.









